The digital market is increasing rapidly, with more people staying online than offline. Online marketing, shopping, gaming, making transactions, viewing news/sports, etc., have increased tremendously.
You may have encountered times when sites slow down or hang up as an internet user. This usually happens due to heavy network traffic. Also, the reason could be too many images, and plugins which can be looked in to avoid slowing down.
SSL Offloading can help you enhance the speed of the server. It is important that you don’t overlook security measures and take care of your website.
It may happen that many people are not technical, hence, here, we will discuss SSL Offloading. Also, we are going to discuss its needs, its functioning, its pros and cons.
What is SSL Offloading?
An SSL offloading reduces the burden of web servers by removing the SSL-based encryption from incoming traffic. This means a separate device can handle the processing of decrypting and encrypting the traffic sent through SSL instead of the web server having to do it all. SSL offloading is designed for SSL acceleration or SSL termination. SSL offloading can help you boost the performance of your web servers and as a result, improve customer experience
Using ASIC ( application-specific integrated circuit) processors, the SSL/TLS encryption/decryption and SSL handshake processes are handled. ASIC processors are also known as Load balancer or a Proxy server.
Would it be advisable to implement SSL offloading?
Few companies want to make their computer systems even more complex. But there are many reasons to consider SSL offloading.
Among the known benefits are:
- Server preservation
When your main servers aren’t forced to deal with encryption and decryption, they’re free to serve your visitors. - Regulation of traffic
Some load-balancing systems allow you to reduce traffic as needed to avoid a crash. - Added security
Your additional server could intercept malicious traffic that could be overlooked or missed by the main server.
If you have a very large website with a lot of traffic, SSL offloading can be very useful.
But, if your website is very small and you can handle the traffic, additional complexity may not make sense for you.
The difference between SSL and SSL offloading is that SSL is commonly used for secure data transfers because encrypted traffic is immune to malicious activity. Alternatively, SSL offloading decrypts the data and forwards it to the web server using a load balancer.
To configure SSL offloading, organizations route SSL requests to a web server through an application delivery controller that intercepts SSL traffic, decrypts it, and sends it to the web server. Importing a valid certificate and key and binding them to the web server are crucial steps in SSL offloading to guarantee the proper exchange of unencrypted communications.
How Does SSL Offloading Work?
SSL offloading devices are used to separate the function of the SSL security certificate. This helps to free the server by alleviating the processes of encryption and decryption. This is done using a different SSL proxy device stationed between the server and the browser.
ASIC processor, as stated above, is that SSL offloading device that functions as a load balancer (proxy server). These processors are designed in such a way that they secure the SSL protocol and it is functioning, thus lessening the burden on the servers.
During SSL offloading, the client sends the encrypted data to the load balancer and decrypts the information. Also, send the plain text to the server.
This offloading device also inspects the network traffic by blocking suspicious traffic.
Some top-load balancers are Kemp LoadMaster, Citrix ADC, Nginx, etc.
Why Need SSL Offloading?
In the area of web security, the use of robust public and private 2048-bit RSA keys ensures a high level of protection for sensitive data. However, this robust security has a disadvantage: it is resource-intensive and can slow down the encryption/decryption process.
To avoid this, a session key is introduced. With 256-bit encryption, this key is not only secure but also faster than traditional public and private keys. This optimization ensures a more efficient and faster user experience.
This increases the load on the server. When numerous users want to access a website at the same time, the server has to process different session keys and encryption/decryption requests. This high workload can affect the performance of the server and lead to slow response times.
To curtail this burden from the server and to enhance the smooth functioning of its backend functions, SSL offloading process and devices were introduced.
To understand the need for SSL offloading, we first need to understand what SSL/TLS encryption is:
SSL/TLS is mainly used to provide an advanced level of security between websites and servers.
Without SSL encryption, chances are hackers will perform MIM attacks against the network, and if they’re successful, you would lose a lot of sensitive information such as cookies or other authentication data.
So, with SSL offloading, you can rest assured that the entire network is deemed secure, as well as packets that pass from the client and server are encrypted.
Types of SSL Offloading:
As stated above, the SSL offloading process is carried out by using a load balancer stationed between the browser and the server. This load balancer device takes care of all the encryption/decryption tasks. This device uses the server’s SSL certificate and private key to carry out the task.
There are two types of SSL offloading, and they are as follows:
- SSL Termination
- SSL Bridging
SSL Termination:
SSL termination is the process of decrypting encrypted traffic before transferring it to a web server.
The SSL Termination method of SSL offloading helps in hastening the server speed. This method connects the browser with the load balancer via HTTPS (encrypted connection). Later the load balancer is connected to the server via HTTP (unsecured connection).
This means the connection between the browser and the load balancer is encrypted and secure. In contrast, the connection between the load balancer and the server is unencrypted and unsecured. If you consider whether it sacrifices security, there is no need to worry, as the HTTP connection takes place on the internal network, which is protected by firewalls. The client has a secure connection with the SSL terminator, which is a pass-through.
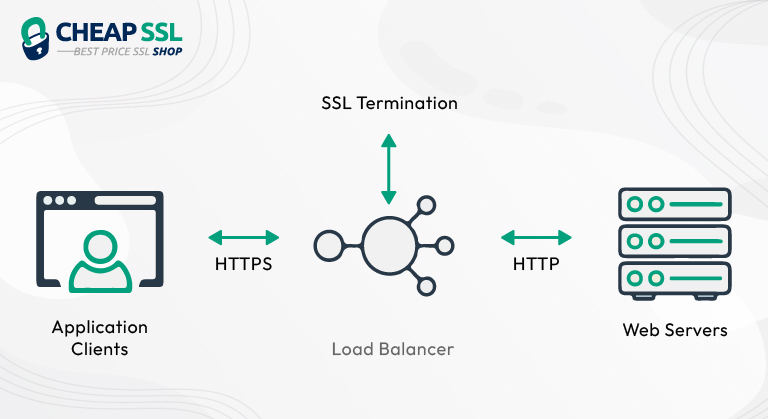
Functioning:
- The load balancer is connected to both parties, i.e., the server and the user’s browser.
- When the user requests a secured (HTTPS) connection, a session key is generated using the server’s public and private keys. This session key is used between the load balancer and the browser to establish encrypted communication.
- The browser’s encrypted data is passed to the load balancer, which decrypts the data using the session key and later passes the decrypted data to the server.
Since the server receives the data in plain format, it sends its response to the load balancer in the same format (decrypted format). - The load balancer uses the session key to encrypt this data again and sends it to the browser, which later decrypts it using the same session key.
Advantages:
- Since the server is relieved from the burden of encrypting/decrypting the data, its workload is reduced, and speed is enhanced.
- This process is ideal for sites that do not deal with sensitive stuff like blogs, informative sites, etc.
Disadvantages:
- If the SSL termination takes place in an internal network and the communication between the SSL offloading device and the web server is not sufficiently secure, there is a risk of interception or manipulation within the internal network.
- SSL termination interrupts the end-to-end encryption between the client and the web server. While the data is secure within the internal network, it is available in unencrypted form when communicating between the SSL offloading device and the web server.
- When SSL offloading devices are added, it brings in extra components to the network infrastructure. This may lead to increased complexity and require additional effort in terms of management and maintenance.
SSL Bridging:
SSL bridging is another method of SSL offloading. SSL bridging is ideal for sites that store and deal with sensitive data, i.e., banking sites, financial institutions, healthcare sites, etc. Sites handling sensitive data cannot use SSL termination since it is a risky SSL offloading process.
HTTPS sites need to handle a lot of traffic from the users, which hampers the servers’ functioning since these servers need to block malicious traffic and other intrusions before passing the data. In such cases, SSL Bridging comes to the rescue.
Like SSL termination also known as SSL termination with re-encryption, this method also involves a load balancer between the browser and the server. Only the functioning of this method is slightly different from the SSL termination method.
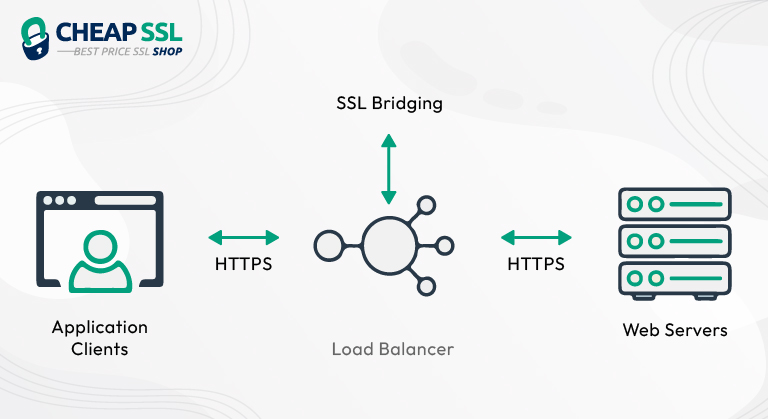
Functioning:
- The user’s browser sends encrypted data to the load balancer via an HTTPS connection.
- The load balancer decrypts the data and carries out an SSL inspection.
- This SSL inspection is done to catch malicious traffic and block it. SSL bridging enables load balancers to inspect and secure decrypted traffic using content inspection, threat detection, and other security policies.
- After the inspection, the load balancer encrypts the decrypted data and sends it to the server later. Thus, the data remains secure during the entire process.
- Later, the server carries out the encryption/decryption process.
Hence, in the SSL bridging method, the main motto of the load balancer is to block malicious content proceeding from the client.
Advantages:
- The main benefit of this method is that the data is secured during the entire browser-server conversation since it is always exchanged in an encrypted format.
- This method helps prevent malicious attacks like MIM, DDoS (distributed denial of services), malware, etc.
Disadvantages:
- Since the server carries out the encryption/decryption functions, the workload is still the same; hence, the burden on the server is not reduced. Decrypting and re-encrypting SSL cab impose a significant load on the load balancer, especially in high-traffic scenarios, requiring proper scaling and resource management.
- The re-writing process of SSL bridging is a major con. The load balancer is authorized to inspect and edit browser data if it is AI (Artificial Intelligence) finds it suspicious.
It later re-writes and re-encrypts safe content and passes it to the server. Any malfunctioning by the AI may cause the load balancer to block sensitive stuff too, which may be missed out on being transferred.
Benefits of SSL Offloading:
SSL offloading offers many benefits and is handled by a third-party security device. Here are a few advantages to SSL offloading:
- SSL offloading makes sure that websites and software are protected. It secures them against cyberattacks like DDoS and man-in-the-middle.
- Prevent server overload and downtime.
- Hasten the SSL connection and improve performance.
- It offloads the encryption/decryption process from the servers, thus reducing their burden and helping them to focus on their main functions.
- It helps in saving server resources.
- If the SSL bridging load balancer is used, it may help block malicious traffic, SSL inspection, HTTPS traffic inspection, etc. This helps in detecting attackers hiding in HTTPS traffic and blocking them.
- It enhances the page load speed, thus raising site visibility in SEO (search engine optimization).
- The server response time is minimized, and its performance is enhanced.
- The website stability and speed are improved.
Wrapping Up:
SSL offloading reduces server’s burden and optimizes server resources. SSL offloading saves page-loading time. If you want to buy an SSL certificate then, you can find low-priced or Cheap SSL certificates available with varied SSL certificate providers, which can help secure your web with encryption. However, apart from site security, site speed is also essential.
If your site load time is more than 2-3 seconds, it may increase your bounce rate since visitors are likely to abandon such sites. SSL offloading helps speed up your server and ensures a good position against competitors.
Since you now have a fair idea about SSL offloading techniques and their pros and cons, you can select any offloading techniques ideal for your business.
As far as the load balancer providers are concerned, select them wisely since you need to trust them with your server’s private key and site-sensitive data.